Accessing data
The AWS ground segment and access to global data
As part of the ground segment setup under the industrial contract for ESA the global AWS data, full orbits of stored mission data, are acquired in real-time at Svalbard. The data are then sent to the KSAT satellite operations center in Tromsø, Norway, processed to level-1b, and then sent further on to EUMETSAT in Darmstadt. EUMETSAT will then distribute the data over EUMETCast (Terrestrial), first to NMSes of the EUMETSAT member states, and later to all EUMETCast users. The timeliness of these global data is expected to be around 110 minutes.
A Nordic Direct Broadcast ground segment providing real-time data
For this project a direct broadcast ground segment has been setup in collaboration with EUMETSAT (see the Ground Segment Development Plan) covering Northern Europe and parts of the Arctic. AWS data are received in real-time from the Direct Readout stations in Greenland, Norway and Finland.
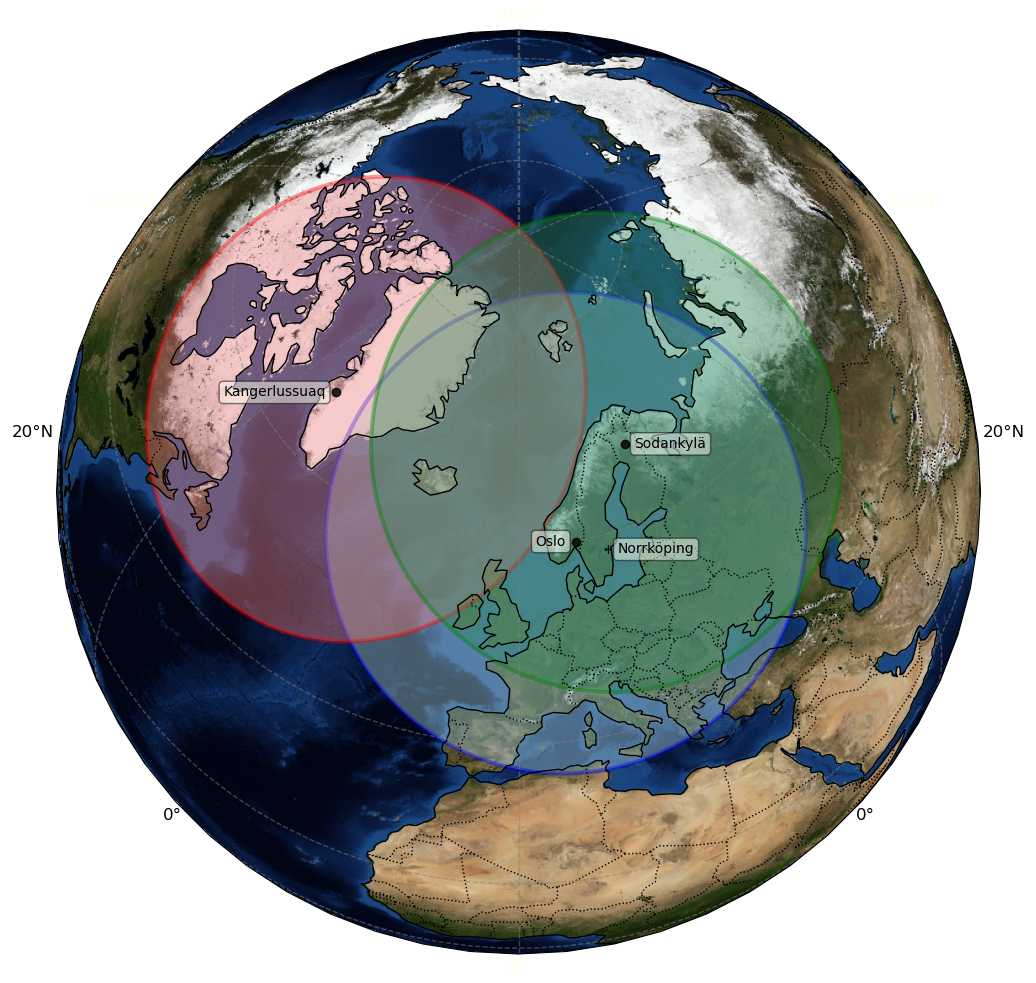 Antenna horizons for a satellite at 595 km for the three Direct Readout
stations considered for AWS reception. This corresponds to the approximate AWS
data coverage of the Nordic ground segment. The SMHI station in Norrköping is
not yet AWS compliant, and will be used only to compensate the Oslo station
with data from other satellites (JPSS) which has to be sacrificed there when
prioritising AWS.
Antenna horizons for a satellite at 595 km for the three Direct Readout
stations considered for AWS reception. This corresponds to the approximate AWS
data coverage of the Nordic ground segment. The SMHI station in Norrköping is
not yet AWS compliant, and will be used only to compensate the Oslo station
with data from other satellites (JPSS) which has to be sacrificed there when
prioritising AWS.
The Greenland data are sent via DMI in Copenhagen, Denmark, to SMHI in Norrköping, Sweden for further processing. The data from the Oslo and Sodankylä stations are processed locally. As all three stations have also other commitments than AWS reception not all visible passes will be acquired.
On average around 60% of the AWS passes visible from Kangerlussuaq are routinely being acquired. For the region covered by the Oslo and Sodankylä antennas AWS reception efficiency is higher, resulting in an overall ~80% AWS reception efficiency over the entire Nordic AWS ground segment.
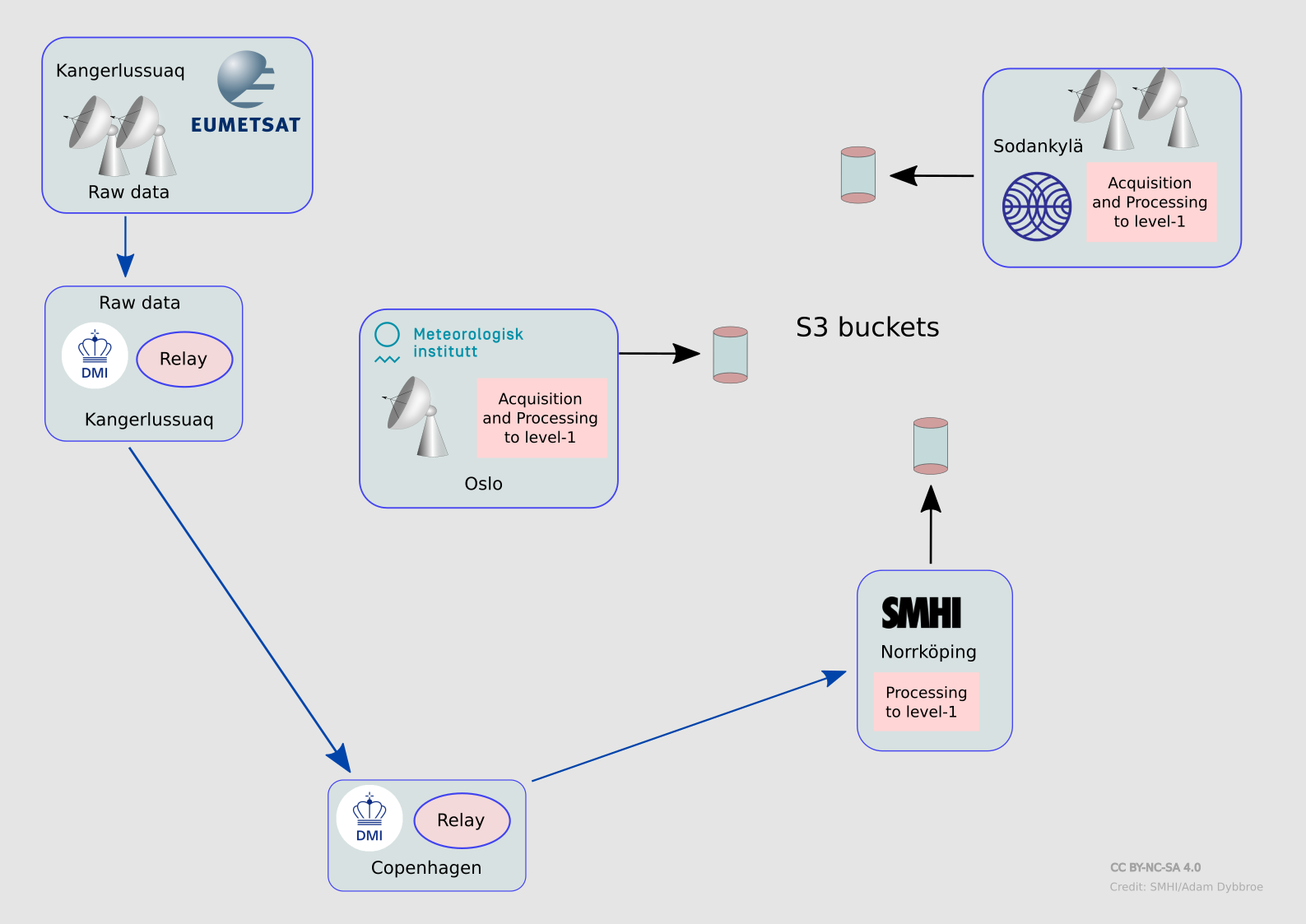 Schematic showing the flow of data and the distributed processing concept of
the Nordic DB ground segment. Data will end up in three S3 buckets, one for
each reception site. The raw data acquired in Kangerlussuaq will be sent to
Copenhagen and uploaded in real-time for SMHI to process and disseminate.
Schematic showing the flow of data and the distributed processing concept of
the Nordic DB ground segment. Data will end up in three S3 buckets, one for
each reception site. The raw data acquired in Kangerlussuaq will be sent to
Copenhagen and uploaded in real-time for SMHI to process and disseminate.
Data are processed in real-time to level-1b (four geolocation datasets, one for each feedhorn/group of channels) and level-1c (all data mapped to the 183 GHz grid). The file format is netCDF/CF and inherrits as far as possible from the EUMETSAT EPS-SG MWS file format. The average timeliness (from observation to level-1c) is better than 15 minutes: Level-1c data are available within 1-3 minutes after end of acquisition, and the passes are usually around 10 minutes long, meaning the first lines received are around 11-13 minutes old, while the last lines received are only a couple of minutes old.
Data access
Data may be available on request, but is intended first of all for NWP centres and first of all for operational (or pre-operational) use over the domain covered by the three stations (see figure above).
To download processed Arctic Weather Satellite data from the three Nordic S3 buckets you
will need to get access/secret key pairs, one pair of keys for each
bucket. Also, of couse you need to know the URLs and the bucket names. For all
that, please contact us at: ![]()
Example - how to fetch data
Below is an example of how to fetch the latest Level-1c data from the bucket at SMHI (data received at Kangerlussuaq, Greenland) from a Linux terminal.
First set environment variables for the keys:
export SMHI_RO_AWS_ACCESS="<the access key you get from us>"
export SMHI_RO_AWS_SECRET="<the secret key you get from us>"Then after adapting the path to where you store the AWS data locally you can run the example python code below to download the last 6 hours of level-1c data from the Kangerlussuaq station:
import os
import s3fs
from pathlib import Path
from trollsift import Parser
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
PATTERN = "W_XX-{centre:s}-{station:s},SAT,{satname:s}-{sensor:s}-{level:s}-RAD_C_{centre:s}_{processing_time:%Y%m%d%H%M%S}_G_D_{starttime:%Y%m%d%H%M%S}_{endtime:%Y%m%d%H%M%S}_T_B____.nc"
awsat_local_dir = '/some/path/to/my/local/aws/data/' # Please adapt to the choice of your own
s3 = s3fs.S3FileSystem(client_kwargs={
'endpoint_url': 'https://satobjectstore.smhi.se/'},
anon=False,
key=os.environ["SMHI_RO_AWS_ACCESS"],
secret=os.environ["SMHI_RO_AWS_SECRET"])
all_esa_l1c_files = s3.ls('satellite-data-kangerlussuaq-arctic-weather-satellite/awsat/l1c/esa')
p__ = Parser(PATTERN)
now = datetime(2024, 1, 15, 12, 0)
tdelta = timedelta(hours=6) # Last six hours of data
for awsatfile_str in all_esa_l1c_files:
awsatfile = Path(awsatfile_str)
localpath = Path(awsat_local_dir) / awsatfile.name
res = p__.parse(awsatfile.name)
obstime = res['starttime']
if (now - obstime) < tdelta:
s3.get(awsatfile_str, str(localpath))